
Column:News Release time:2025-10-10 Number of readers:129
✅ “Applications of Dewo Microswitches in Electric Vehicle Charging Guns”
✅ “Waterproof Microswitches: Principles and Practical Applications”
Microswitches are the unsung heroes behind the smooth operation of countless electronic devices and industrial systems. From household appliances to automated machinery, these tiny yet powerful components play a vital role in controlling electrical circuits with precision and reliability.
However, even the best microswitch can lose effectiveness if it’s not properly installed, maintained, or protected from environmental stress. Ensuring the stability and reliability of microswitches is essential to maximizing performance, preventing downtime, and extending their service life.
In this guide, we’ll explore the best practices for maintaining microswitch performance — from understanding how they work to installation, maintenance, and advanced reliability strategies.
To ensure the stability and reliability of the microswitch, it is essential to understand its operating principle and internal structure. The microswitch controls circuit connections by detecting small mechanical displacements and typically consists of key components such as contacts, springs, and an actuator button. When an external force is applied to the actuator, it moves until reaching a snapped-in position, thereby closing the circuit. Upon release of the force, the actuator returns to its original position, reopening the circuit. This snap-action mechanism enables rapid switching with minimal contact wear, which is a primary factor contributing to the device's durability and operational reliability.(As shown in the figure below)
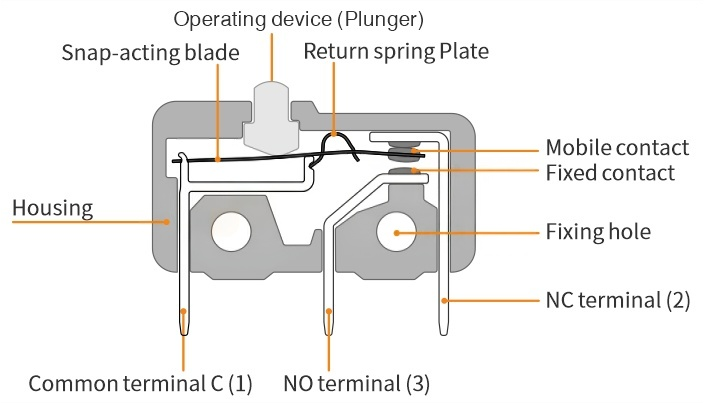
Correct installation is crucial for the long-term reliability of a microswitch. Even high-quality micro switches can fail prematurely if installed incorrectly.
Before installation, consider:
Load Rating: Match the microswitch’s voltage and current rating to your circuit.
Actuator Type: Use the actuator style best suited for your device’s motion or pressure needs.
Environmental Conditions: Use weatherproof or high-temperature switches when necessary.
Mounting Style: Select the appropriate mounting type — surface, panel, or embedded.
Clean the Installation Area: Remove dust or debris to prevent interference.
Align Precisely: Ensure the actuator aligns correctly with the moving part it interacts with.
Secure Mounting: Use the right screws and avoid over-tightening.
Correct Wiring: Follow the manufacturer’s wiring diagram and secure all connections.
Test Before Final Assembly: Activate the switch manually to verify correct operation.
Always disconnect power before installation.
Use personal protective equipment (PPE) if required.
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and local electrical codes.
Proper installation prevents operational issues and ensures that your microswitch performs reliably from day one.
Regular maintenance is key to preventing failures and extending the lifespan of microswitches.
Visual Checks: Look for cracks, corrosion, or loose wires.
Functional Testing: Activate the switch manually — a crisp “click” indicates proper function.
Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to verify electrical operation.
Disconnect Power: Always before cleaning.
Use Compressed Air: Remove dust and debris from tight areas.
Wipe with Isopropyl Alcohol: Clean the exterior gently with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate If Needed: Apply a small amount of approved lubricant if the actuator feels stiff — but avoid overdoing it.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
| Sticking Actuator | Dirt buildup or misalignment | Clean and realign |
| Inconsistent Response | Loose wiring or corrosion | Tighten and clean connections |
| No Electrical Continuity | Worn contacts | Replace microswitch |
| Environmental Damage | Exposure to moisture or heat | Use sealed or temperature-rated models |
Preventive maintenance keeps your microswitches operating smoothly and minimizes unexpected breakdowns.
Beyond maintenance, overall reliability depends on how microswitches are used and the environment they’re in.
Stay within rated voltage and current limits.
Avoid excessive force on the actuator.
Use correct actuators for the intended purpose.
Implement safety interlocks in critical systems.
Choose sealed or waterproof microswitches in humid or dusty areas.
Use sealed connectors and heat-shrink tubing to protect wiring.
Control ambient humidity and temperature to prevent corrosion.
Regularly inspect for signs of wear or failure.
Establish a replacement schedule for high-use applications.
Keep spare switches available to minimize downtime.
Document all replacements and repairs for future maintenance planning.
For users seeking enhanced reliability in demanding environments, these advanced strategies can make a difference:
Select reputable brands such.
Check material quality, industry certifications (UL, CE), and lifecycle ratings.
Consider custom microswitches tailored to your application’s specific needs.
Know the switch’s rated operating force and ensure actuators match it.
Avoid overloading the actuator or applying uneven pressure.
Periodically test and recalibrate in automated systems to maintain precision.
Use the correct wire gauge for the electrical load.
Employ strain relief to prevent wire fatigue.
Secure all connections tightly and insulate them properly.
Use shielded cables in environments with strong electromagnetic interference (EMI).
These small yet impactful steps can dramatically improve both microswitch reliability and device performance.
Ensuring the stability and reliability of micro switches involves a series of interrelated factors. These include understanding their internal operating mechanisms, selecting high-quality components, ensuring proper installation and operation, performing regular maintenance, and complying with applicable industry standards. Each step is critical to achieving optimal performance. Only through meticulous attention to all aspects can micro switch devices function reliably across diverse applications and deliver consistent, dependable performance in both industrial systems and everyday use.